Talent Heatmap Analytics: A Tool for Modern Talent Strategies
- Marcus

- Dec 17, 2025
- 4 min read
Amid evolving labor markets, organizations face skill shortages, rapid shifts in required competencies, and high workforce mobility. Strategic talent planning is now critical.
Talent Heatmap Analytics provides clear, visual insights into workforce needs, supporting more strategic decisions.
What does Talent Heatmap Analytics entail, and how can organizations utilize it effectively without significant expenditure?
What Are Talent Heatmap Analytics?
A Talent Heatmap visually displays talent and skill distribution across dimensions such as locations, departments, or experience levels. It combines internal data (qualifications, performance, engagement) with external data (talent supply, salaries, competitors).
These datasets are aggregated and shown using color gradients or interactive dashboards.
Heatmaps provide instant insights into where competencies are concentrated and where gaps or risks exist.
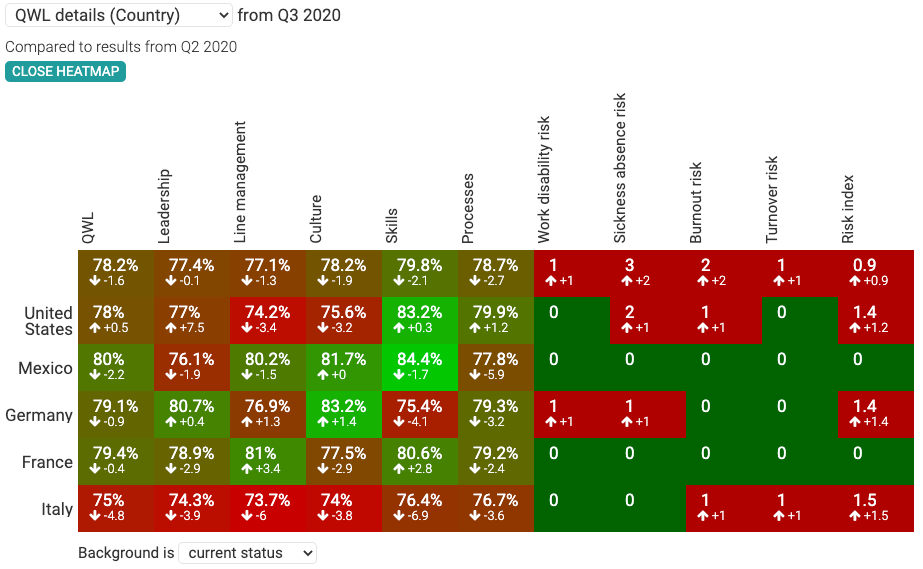
Use Cases in Talent Acquisition and People Development
So how can this be applied in practice? Here are some typical examples:
Talent Acquisition / Recruiting
Heatmaps can reveal where specific skills are particularly concentrated (hot spots) — and where competition or skill scarcity is high (cold zones).
This facilitates targeted recruiting by leveraging regions with high talent availability, considering alternative locations, or focusing on remote talent sources.
Heatmaps also identify skill trends and competitor activities, highlighting which capabilities are gaining industry demand.
Learning, Development & Internal Mobility
Visualizing internal competencies makes it easier to identify development needs: Which capabilities are missing? Where is untapped potential?
Mapping internal mobility (e.g., transfers, promotions) supports succession planning and career path design, fostering growth from within rather than relying on external hiring.
When combined with compensation or rewards data, heatmaps can also surface retention or equity risks.
Strategic Workforce Planning
By adding forecast data, organizations can simulate “what-if” scenarios —
What if we need X new skills in two years? Or what if turnover rises in function Y?
A heatmap becomes a powerful visual management tool.
This transforms HR operations from reactive approaches (hiring as needed) to strategic planning (anticipating where future talent will be required).
Benefits of the Approach
Implementing Talent Heatmap Analytics offers several key advantages:
Greater transparency: Complex information becomes tangible — such as skill clusters, geographic distributions, and internal potential.
Strategic steering: Moves HR from a purely operational focus to a proactive, forward-looking strategy.
Efficiency gains: Targeting hot spots or leveraging internal capabilities can reduce costs and speed up hiring.
Early risk & gap detection: Skills gaps become visible early, enabling proactive development, mobility, or recruiting initiatives.
Closer alignment with business goals: Mapping skill needs to market realities aligns HR more tightly with organizational success.
Enhanced internal mobility & engagement: Employees gain visibility into their capabilities and growth opportunities — boosting motivation and retention.
Risks and Challenges
However, several challenges must be considered:
Data quality & integration: HR data often lives in silos, is incomplete, or lacks standardization — reducing analytical reliability.
A heatmap presents the what, not the why. Interpreting correlation as causation must be avoided.
Technical complexity & cost: Fully integrated platforms with real-time data and AI can be expensive, especially for smaller organizations.
Adoption & change culture: Moving to data-driven decisions requires mindset shifts across HR and leadership. Without buy-in, impact is limited.
Data privacy & ethics: Handling employee data responsibly means complying with laws (e.g., GDPR) and maintaining trust through transparency.
Data overload: Too many indicators without a clear purpose can lead to analysis paralysis — plenty of data, no clear action.
A Pragmatic Approach — Even on a Modest Budget
While some enterprise solutions are complex, smaller or mid-sized organizations can begin with pragmatic steps. For example:
Pick one focused use case, such as:
A specific skill domain (e.g., digital or data literacy)
One region or location
A function or department with known challenges
This keeps the effort manageable and results visible faster.
Start with Available Data
Use existing HR systems: employee records, qualifications, performance data. Add simple inputs, such as self-assessments or short employee surveys. Include external sources like labor market statistics or public skill reports — many are free or low-cost.
This creates a solid starting dataset without expensive tools. Tools like Excel/Google Sheets with heatmap add-ons, Power BI, or Tableau Public (some free) are often sufficient.
Visualize skills by color, cluster locations, or show concentration patterns. Keep your visualization intuitive and actionable.
From your heatmaps, identify:
Where skill gaps exist
Where competition is toughest
Where internal development makes more sense than external hiring
Start with small pilot initiatives — for example:
Launch a micro learning or reskilling program.
Test remote work or talent relocation.
Measure impact using metrics such as time-to-fill, internal mobility rate, or skill uplift.
Build Iteratively
Start small and scale: expand to more skills, sites, or functions once the initial value is proven.
Gradually improve data quality and governance (standardize skill terms, update profiles regularly).
Evolve your dashboards by adding more layers (e.g., pay, mobility, market data).
Drive Change & Communication
Build transparency: explain to employees how the data is used and why.
Train leaders to interpret insights and work with HR to build trust and momentum.
Conclusion
Talent Heatmap Analytics offers a powerful opportunity to make talent acquisition, development, and workforce planning more data-driven, aligned, and actionable.
The benefits range from greater transparency and smarter decision-making to measurable efficiency gains. However, success requires care: poor data, overinterpretation, or lack of buy-in can easily undermine the effort.
The good news: You don’t need a polished enterprise platform to start.
The main takeaway: even with simple tools and focused action, organizations can unlock practical talent insights and set the stage for future growth.
By starting now with Talent Heatmap Analytics, HR teams move from reactive to proactive strategies, gaining a clear edge in shaping future talent.









Comments